The Shocking Truth About Vitamin A Overdose: How Too Much Can Destroy Your Liver
Vitamin A is an essential fat-soluble vitamin that plays a critical role in maintaining healthy skin, vision and immune function. Although it offers several health benefits, it is important to find the right balance. Taking too much vitamin A can lead to serious health complications, including liver damage. This article examines the benefits, deficiencies, and dangers of overdosing on vitamin A. Why people take vitamin A Vitamin A is essential for several reasons: Healthy vision: Vitamin A is important for maintaining healthy vision and preventing night blindness. Immune system support: It helps protect the body from...
The Shocking Truth About Vitamin A Overdose: How Too Much Can Destroy Your Liver
Vitamin A is an essential fat-soluble vitamin that plays a critical role in maintaining healthy skin, vision and immune function. Although it offers several health benefits, it is important to find the right balance. Taking too much vitamin A can lead to serious health complications, including liver damage. This article examines the benefits, deficiencies, and dangers of overdosing on vitamin A.
Why people take vitamin A
Vitamin A is essential for several reasons:
- Gesundes Sehen: Vitamin A ist wichtig für die Aufrechterhaltung eines gesunden Sehvermögens und die Vorbeugung von Nachtblindheit.
- Unterstützung des Immunsystems: Es hilft, den Körper vor Infektionen zu schützen, indem es ein robustes Immunsystem aufrechterhält.
- Hautgesundheit: Vitamin A ist wichtig für das Zellwachstum und die Hautregeneration und hält die Haut gesund und jugendlich.
- Reproduktive Gesundheit: Es unterstützt die reproduktive Gesundheit bei Männern und Frauen.
Symptoms of vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin A deficiency symptoms include:
- Nacht Blindheit
- Trockene, schuppige Haut
- Erhöhte Anfälligkeit für Infektionen
- Schwierigkeiten, eine Schwangerschaft zu empfangen oder aufrechtzuerhalten
Benefits of Vitamin A
The health benefits of vitamin A include:
- Verbesserte Immunfunktion
- Verbesserte Sicht
- Gesunde Haut
- Bessere reproduktive Gesundheit
Foods rich in vitamin A
Vitamin A is found in various food sources including:
- Süßkartoffeln
- Möhren
- Spinat
- Grünkohl
- Brokkoli
- Eier
- Milchprodukte
However, it is important to consume these foods in moderation to avoid vitamin A overdose.
Dangers of overdosing on vitamin A
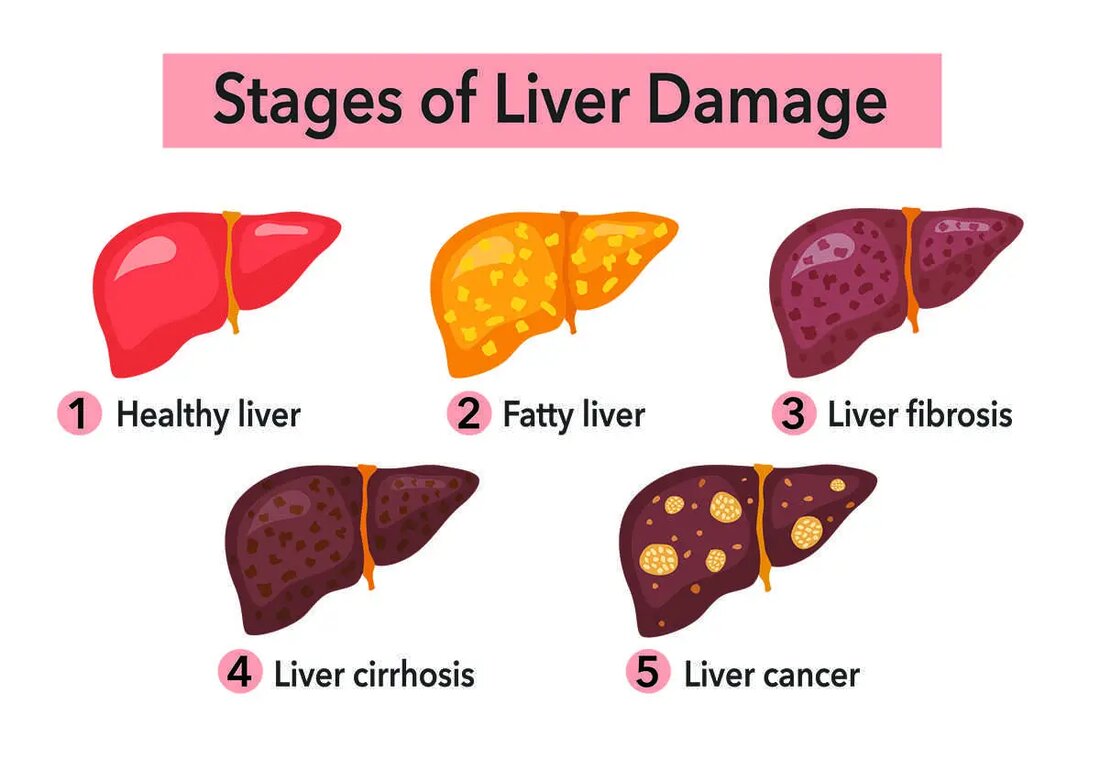
Excessive consumption of vitamin A, known as hypervitaminosis A, can cause serious health problems, including liver damage. According to a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, excessive vitamin A intake is associated with an increased risk of liver damage and bone fractures (Feskanich et al., 2002). Another study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that high levels of vitamin A in the blood can lead to cirrhosis, a condition characterized by irreversible scarring of the liver (Penniston & Tanumihardjo, 2006).
How vitamin A damages the liver
Vitamin A is fat-soluble, meaning it is stored in the body's fatty tissue, including the liver. When consumed in excess, vitamin A accumulates in the liver and causes toxicity. Over time, this can lead to liver inflammation, fibrosis and eventually cirrhosis.
Warning signs and symptoms of vitamin A overdose
Signs of a vitamin A overdose include:
- Übelkeit und Erbrechen
- Schwindel
- Kopfschmerzen
- Ermüdung
- Appetitverlust
- Trockene, raue Haut
- Gelenkschmerzen
- Schwellung der Leber
- Gelbfärbung von Haut und Augen (Gelbsucht)
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Maintaining a Healthy Balance of Vitamin A
To avoid a vitamin A overdose, follow these guidelines:
- Nehmen Sie eine ausgewogene Ernährung zu sich, die reich an Obst, Gemüse und anderen Vitamin-A-Quellen ist.
- Vermeiden Sie eine übermäßige Einnahme von Vitamin-A-Präparaten, insbesondere wenn Sie bereits Vitamin-A-reiche Lebensmittel zu sich nehmen.
- Konsultieren Sie einen Arzt, bevor Sie mit einem neuen Nahrungsergänzungsmittel beginnen, insbesondere wenn Sie bereits Lebererkrankungen haben oder schwanger sind.
It is important to follow the recommended daily intake of vitamin A to avoid overdosing. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for vitamin A varies depending on age and gender. For adult men, the RDA is 900 micrograms (mcg) retinol activity equivalents (RAE) per day, while adult women need 700 mcg RAE per day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult their doctor for specific recommendations. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for vitamin A, which is the maximum daily intake that is unlikely to cause adverse health effects, is set at 3,000 mcg RAE per day for adult men and women. Regularly consuming more than the UL can cause vitamin A toxicity and increase the risk of liver damage and other health complications.
While vitamin A is essential for maintaining overall health, it is important to be aware of the dangers of overdosing on this nutrient. By eating a balanced diet and monitoring your vitamin A intake, you can reap the benefits of this essential vitamin without compromising your liver health.
Sources:
- Feskanich, D., Singh, V., Willett, W. C., & Colditz, G. A. (2002). Vitamin A intake and hip fractures among postmenopausal women. The New England Journal of Medicine, 346(1), 47-54., https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa140848
- Penniston, K. L., & Tanumihardjo, S. A. (2006). The acute and chronic toxic effects of vitamin A. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 83(2), 191-201., https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/83/2/191/4649420

 Suche
Suche
 Mein Konto
Mein Konto
